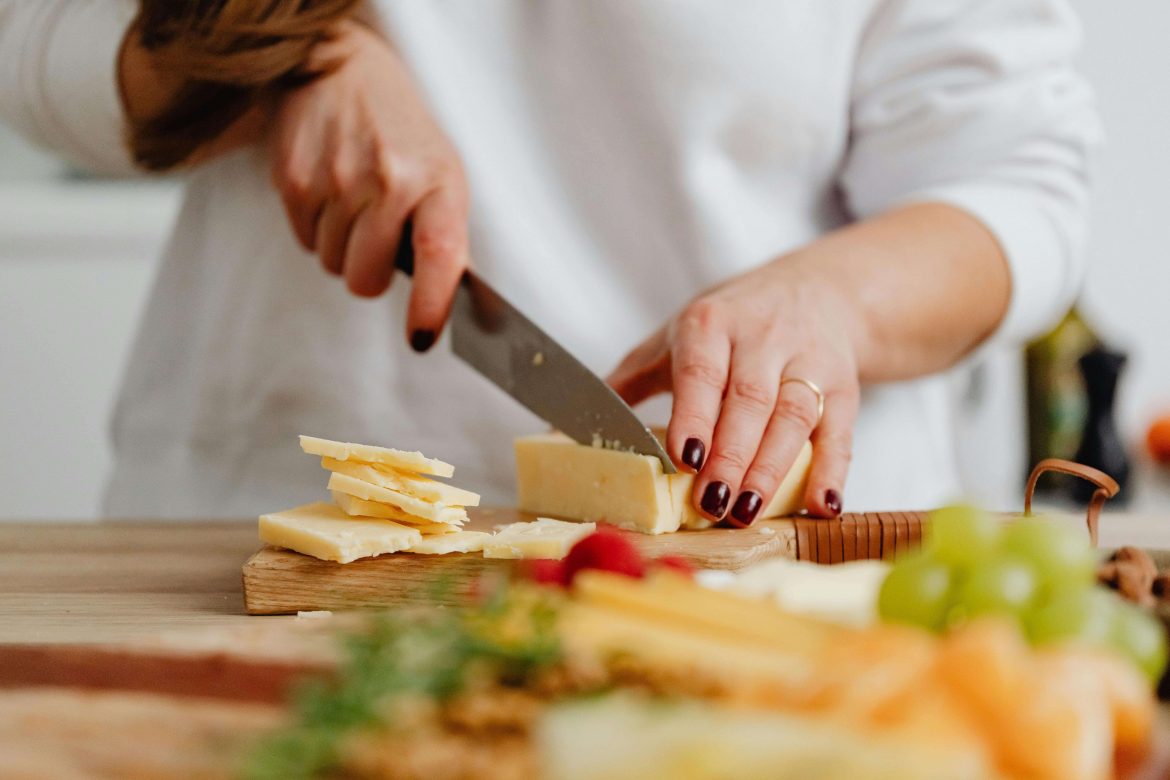
Cheese can indeed be frozen, but it’s important to know that this preservation method might alter its texture. Freezing can make cheese drier and crumblier.
Generally, hard and semi-hard cheeses like cheddar fare better in the freezer compared to softer, artisanal varieties.
Why freeze cheese?
Freezing is a time-honoured technique that has been used for many years. It’s a great way to extend the shelf life of cheese, cut down on waste, and save money. Although cheese is often best enjoyed fresh to maintain its optimal flavour and texture, sometimes it’s necessary to freeze it if you have more than you can use before the expiration date.
How freezing and thawing affect cheese
The impact of freezing on cheese depends largely on its water content. For instance, cottage cheese, which has high moisture, freezes at around -1.2°C, while cheddar, with lower moisture, freezes at about -12.9°C.
Freezing cheese forms ice crystals inside it, which can disrupt the cheese’s structure. When thawed, the cheese can become dry, crumbly, or mealy. On the other hand, cheese that has been frozen for a longer period may not melt as well as fresh cheese.
Freezing also inactivates bacteria, yeasts, and molds in cheese, which helps in preserving it. However, it doesn’t kill these microorganisms entirely, so they might become active again once the cheese is thawed. This can be particularly problematic for cheeses that rely on active molds for their characteristic flavours and textures, such as blue cheese or Camembert.
Best and worst cheeses to freeze
Best cheeses to freeze:
- Cheddar: Hard and semi-hard cheeses like cheddar generally freeze well, though they may become crumbly.
- Mozzarella: Particularly effective when shredded. It might not melt as well after freezing, but it’s suitable for cooked dishes.
- Pizza Cheese: Like shredded mozzarella, it can be frozen for later use in recipes.
- Colby: This semi-hard cheese freezes well and maintains its texture fairly well.
- Gouda: Another good candidate for freezing, though it may become a bit drier.
Worst cheeses to freeze:
- Brie and Camembert: Soft, ripened cheeses with delicate textures don’t freeze well and can lose their quality.
- Ricotta and Cottage Cheese: High moisture content makes them unsuitable for freezing as they can become watery and separated.
- Parmesan and Romano: Hard, grated cheeses are best stored in the fridge where they can last up to a year without freezing.
- Fresh Cheeses: Cheese like queso fresco or paneer can become too crumbly and dry when frozen.
- Processed Cheeses: These often don’t freeze well and may suffer in quality.
How to freeze cheese
- Preparation: Cut cheese into portions you’re likely to use at once. For block cheese, keep portions to 1 pound (500 grams) or less. Grate or slice cheese if desired. Wrap cheese in its original packaging or use foil or cheese paper. Separate slices with parchment paper if freezing individually.
- Freezing: Store the wrapped cheese in an airtight ziplock bag or container to prevent freezer burn. Freeze cheese at a temperature of at least -23°C. Use the quick freeze function on your freezer if available. For best quality, use frozen cheese within 6–9 months.
- Thawing: Thaw cheese in the refrigerator at 0–1°C for several hours. Shredded cheese can be used directly from the freezer in cooking. To improve texture, let thawed cheese sit in the fridge for a few days before using.
Remember, once thawed, cheese should not be re-frozen. Frozen cheese is ideal for use in cooked dishes where changes in texture are less noticeable, like in sauces, pizzas, or grilled cheese sandwiches.
ALSO SEE: Check out these cheese-making workshops
Celebrate Goat’s Cheese Day with these cheese-making workshops
Image: Pexels