Living with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) can be challenging, especially when it comes to food choices. Many individuals find that certain foods can trigger uncomfortable digestive symptoms, making it crucial to be mindful of what goes on your plate.
Certain foods can help ease symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). These include foods that are low in carbohydrates known as FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols) that cause gas, bloating, and abdominal pain by slowly fermenting in the intestines.
Here, we explore some common culprits that could exacerbate IBS symptoms, based on insights from the IBS and Gut Health Clinic and Healthline.com, and offer alternatives to ensure those who suffer from IBS have a more comfortable eating experience.
Foods to avoid if you have IBS
Insoluble Fiber
While dietary fiber is essential for gut health, some people with IBS find that foods high in insoluble fiber, such as whole grain products and certain vegetables, can worsen their symptoms. Opting for soluble fiber sources like beans, fruits, and oat products may be a better choice for many individuals.
Gluten
Gluten, a protein found in grains like wheat, rye, and barley, can trigger symptoms similar to those of IBS in some individuals. Experimenting with a gluten-free diet, incorporating alternatives like millet and quinoa, could provide relief for those sensitive to gluten.
Dairy
Dairy products, particularly high-fat varieties, may lead to digestive discomfort for people with IBS. Switching to lactose-free options or plant-based alternatives like soy or almond milk can help alleviate symptoms while ensuring adequate calcium intake.
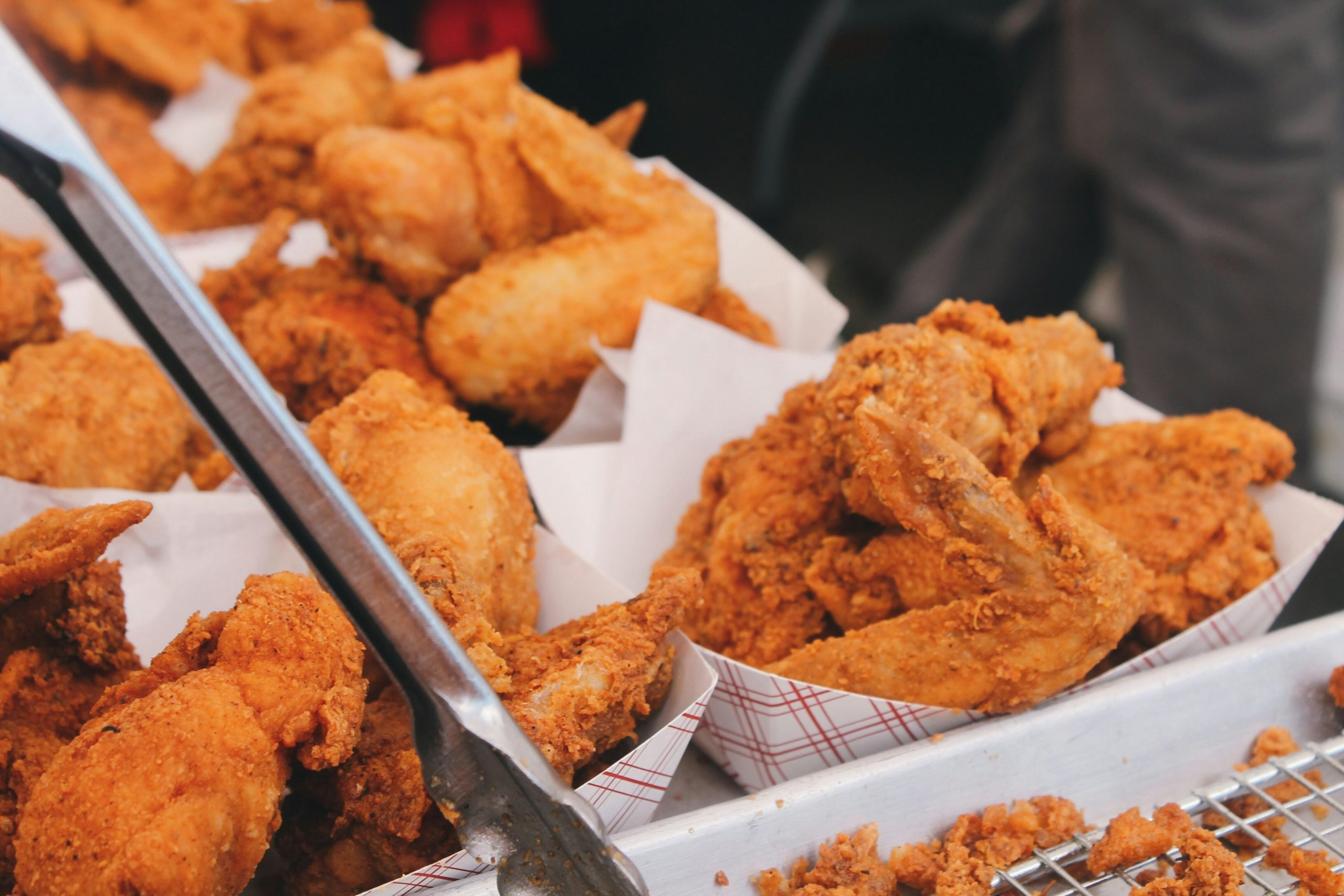
Fried Foods
Fried foods, with their high-fat content and altered chemical composition, can be hard on the digestive system. Opting for healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, or air-frying can reduce the likelihood of triggering IBS symptoms.

Beans and Legumes
While beans and legumes are nutritious sources of protein and fiber, they contain compounds that may exacerbate IBS symptoms in some individuals. Experimenting with soaking and rinsing techniques or avoiding them altogether can help determine their impact on your digestive health.
Caffeinated Drinks
Caffeine-containing beverages like coffee and sodas can stimulate the intestines, potentially causing diarrhea for those with IBS. Choosing caffeine-free alternatives or moderating intake can minimize discomfort.
Highly Processed Foods
Highly processed foods, laden with additives and preservatives, may exacerbate IBS symptoms and contribute to overall health issues. Opting for whole, fresh foods and preparing meals at home whenever possible can be a healthier alternative.

READ MORE: Foods & fruits you need to be eating to boost your immune system ahead of the colder seasons
Sugar-Free Sweeteners and Chocolate
Sugar-free products often contain sugar alcohols or artificial sweeteners that can be difficult to digest, leading to digestive discomfort and laxative effects. Checking ingredient labels and limiting consumption of these sweeteners can be beneficial for managing IBS symptoms. Chocolate, due to its fat, sugar, and caffeine content, can trigger IBS symptoms in some individuals. Exploring vegan options or moderating consumption may help mitigate discomfort.
Alcohol
Alcohol, particularly beer and mixed drinks containing gluten or high sugar content, can exacerbate IBS symptoms and contribute to dehydration. Choosing gluten-free or low-sugar alternatives and moderating alcohol intake can be beneficial.
Garlic and Onions
Garlic and onions, rich in fructans, may cause gas and cramping in individuals with IBS. Experimenting with different cooking methods or using substitutes can help identify triggers.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cabbage can be difficult to digest, potentially exacerbating IBS symptoms. Cooking these vegetables thoroughly or opting for alternative options may reduce discomfort.
Foods you can eat instead
While avoiding trigger foods is essential for managing IBS, it’s equally important to ensure adequate nutrition and while you should steer clear from the foods listed above, you still have a wide array of options with low FODMAP scores to enjoy.
Foods devoid of carbohydrates or low in FODMAPs are permitted in this dietary regimen. This can encompass:
- Fish and other meats
- Eggs
- Butter and oils
- Hard cheeses

Furthermore, other nutritious low-FODMAP foods that you can relish include:
- Lactose-free dairy products
- Certain fruits such as bananas, blueberries, grapes, kiwis, oranges, and pineapple
- Specific vegetables including carrots, celery, eggplant, green beans, kale, pumpkin, spinach, and potato
- Grains like quinoa, rice, millet, and cornmeal
- Firm and medium tofu
- Seeds such as pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, and sunflower seeds
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or dietitian, can help develop a tailored elimination diet while ensuring nutritional needs are met. By making mindful food choices and experimenting with alternatives, individuals with IBS can enjoy improved digestive health and overall well-being.
ALSO SEE: A registered dietitian’s tips on foods for vaginal health
Feature image: Pexels