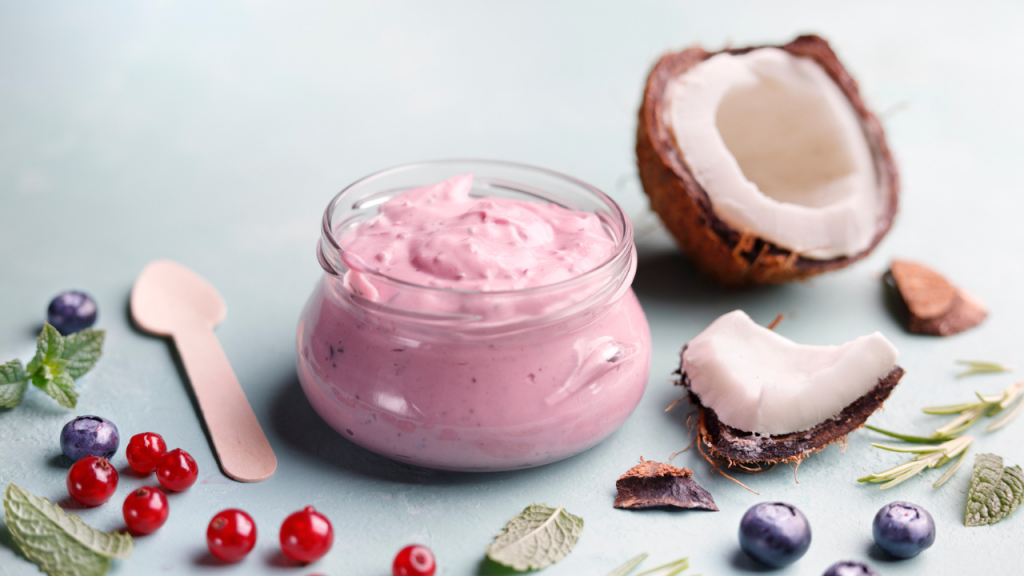
In a world full of so many different types of bacteria with an estimation of 40 trillion which is the number of bacteria that make our gut a home. Every day, we live in harmony with beneficial bacteria, known as gut microbiota, which contribute to the numerous benefits of fermented foods. These foods not only aid in digestion but also provide essential nutrients and support our immune system.
In underdeveloped and developing countries, due to poverty, fermentation is one of the most widely used preservation methods. It not only allows extending the shelf life of food, but also brings other benefits, including inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, improving the organoleptic properties and product digestibility, and can be a valuable source of functional microorganisms.
Today, there is a great interest in functional strains, which, in addition to typical probiotic strains, can participate in the treatment of numerous diseases, disorders of the digestive system, but also mental diseases, or stimulate our immune system.
Hence, fermented foods and beverages are not only a part of the traditional diet, e.g., in Africa but also play a role in the nutrition of people around the world. The fermentation process for some products occurs spontaneously, without the use of well-defined starter cultures, under poorly controlled or uncontrolled conditions.
According to Rediscover Dairy, which is a health professional site on everything dairy, keeping our gut microbe happy and healthy is through, fermented foods, the rising stars on our grocery fermented foods and beverages are made using different combinations of bacteria, such as lactic acid bacteria, and other microbes like molds and yeasts.
According to research done by Rediscover Dairy, fermentation is thought to be the oldest and most economical method of producing and preserving food, with over 3 500 fermented foods making up one-third of our human diet.
A Focus on Fermentation
During fermentation, unique and beneficial changes take place to a food or beverage. The process of fermentation increases the shelf-life to improve preservation, vitally important in food security and food safety. Monique Piderit, registered dietitian says:
“Fermented foods also add to the nutritional value of our diet. This is because these foods can contribute towards making some vitamins and other healthy bioactive compounds more available to the body. Fermented foods can help remove and reduce toxins (like mycotoxins) and anti-nutrients (like tannins and phytic acid) from our diets, as well as help with the digestion of parts of the food that sometimes cause trouble in our guts (like how the lactose in fermented dairy is pre-digested for easier absorption).”
Go for the Gut
Likely the most well-known benefit of eating fermented foods are the great gut-enhancing benefits. Poor diets, stress, medication like antibiotics and anaesthesia, as well as other factors can substantially affect the beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiota.
Made with these healthy microbes, fermented foods are a source of live and active cultures. Regularly enjoying fermented foods in our diets can then help to restore the balance of gut bacteria because of the live cultures that exist naturally in these foods. And what’s more, studies have shown that if we regularly eat fermented foods and beverages, the live cultures can potentially increase the microbes in our gut by 10 000 times.
Now while fancy fermented foods like kefir and kombucha are all the rage, there are two everyday foods that top this list: yoghurt and maas. Fermented dairy is so proudly part of our South African heritage and a supplementary staple food, with great cultural importance. These dairy-based South African favourites are convenient, easy-to-access, storage friendly and cost-effective examples of fermented foods. Choosing these foods regularly also supports the recommendation of our food-based dietary guidelines to “Have milk, maas and yoghurt every day.”
Here’s how to get with the fermented food frenzy, the South African way according to Rediscover Dairy.
Yoghurt, whether plain or flavoured, full cream or fat free, will support a healthy gut and also supplies naturally occurring vitamins, minerals, proteins, and carbohydrates essential for good health. Yoghurt makes for an easy lunchbox filler for children and adults alike. Blend with fresh fruit for an on-the-go smoothie or serve as a healthy dessert dusted with cinnamon.
Maas can be enjoyed as an anytime drink, either on its own or with some added flavour like honey or cocoa powder for a twist. Keep it simple and pour over pap for a quick start to your morning or serve with fruit as you would with yoghurt. Stir into soups or sauces for a creamy taste or use as a recovery drink after exercise.
ALSO SEE: How to make the trending, tasty, and totally addictive yoghurt bark
Written by Johana Mukandila for BONA.
Feature image: Getty